
Introduction
Google Ads, a powerful tool for businesses to reach potential customers, has increasingly become a platform exploited by cybercriminals. While it offers significant marketing advantages, it also presents substantial security risks to individuals. This article explores how Google Ads can compromise personal security and what users can do to protect themselves.
Google Ads has become a serious problem for cybersecurity, serving as a distribution vector for various types of malware. This alarming trend exploits users’ trust in Google’s ecosystem (and advertising platform) to spread malicious software and compromise systems. A recent example perfectly illustrates this threat. In June 2024, a new strain of malware targeting Mac was discovered. These malicious ads mimicked Arc, a popular browser on macOS, redirecting users to a counterfeit website:

Once downloaded and installed, the malware transmitted the user’s data (an infostealer called Poseidon). This is not an isolated incident; attackers regularly use Google Ads to spread various types of malware through deceptive sites. These sites imitate popular legitimate software such as VLC, 7-Zip, and CCleaner, and they pay Google to be ranked above other results (example for Open Broadcaster Software):

The threat is particularly insidious because it exploits the perceived legitimacy of Google and, by extension, its Ads module. Users, accustomed to trusting Google’s sponsored results, may be less vigilant when encountering these malicious ads.
File downloads and unexpected behaviors
Personal ExperienceA company where I interned experienced a crisis (ransomware-related) due to a ransomnote displayed full screen on an employee’s computer. I repeatedly recommended a browser-based ad blocker, but the management believed that firewalls would suffice (considering they were new and freshly configured at the time, I won’t go into details, but domain blocklists are clearly not enough…). In addition to generating stress and temporarily halting the employee’s work, the company had to hire a forensics specialist to trace the origin of this “attack,” which turned out to be a site mimicking a full-screen ransomnote. The user accessed the site due to sponsored links at the top of the Google page (which are blocked by default by ad blockers).
Files downloaded from these malicious sites are often password-protected zip archives, allowing them to bypass antivirus scans on the platforms where they are hosted.
As always, to protect yourself, it is essential to download software only from official sources and remain cautious of unusual installation instructions. Users should be aware that even legitimate-looking ads can potentially host malicious content. While Google claims to take action against malicious advertisers once informed, the responsibility for identifying and removing these threats often falls on end-user antivirus products or other security solutions. This situation highlights the need for increased user vigilance and improved detection and prevention mechanisms by Google.
Real-World Consequences
The implications of these threats are not merely theoretical. Numerous individuals have reported severe consequences after falling victim to malvertising through Google Ads:
-
Identity TheftCybercriminals can harvest personal information from infected devices, leading to identity theft. Victims may find their financial accounts drained or their identities used for fraudulent activities. -
Loss of Digital AssetsInfluencers and digital creators have experienced devastating losses after clicking on malicious ads. For example, one influencer reported losing access to multiple social media accounts and digital assets after downloading software from a sponsored Google link. -
Corporate BreachesBusinesses are not immune either; threat actors have used Google Ads as an entry point for ransomware attacks against corporate systems, jeopardizing sensitive data and operational integrity.
The Backbone of Google’s Revenue
More than 75% of Alphabet’s revenue comes from its advertising services, making it the largest digital ad marketplace in the world. Google Ads allows businesses, both large and small, to reach their target audiences effectively through various platforms, including Google Search, YouTube, and partner websites. This extensive reach not only supports Google’s operations but also provides significant financial backing for numerous online publishers and content creators.
-
Google Search & OtherThis segment is the largest contributor, accounting for about 56.93% of total revenue in 2023, which translates to approximately $175.04 billion. -
YouTube AdsRevenue generated from advertisements on YouTube constitutes around 10.26% of total revenue, amounting to about $31.51 billion in 2023. -
Google NetworkThis includes revenue from ads displayed on partner websites and apps, contributing roughly 10.20%, or about $31.316 billion.
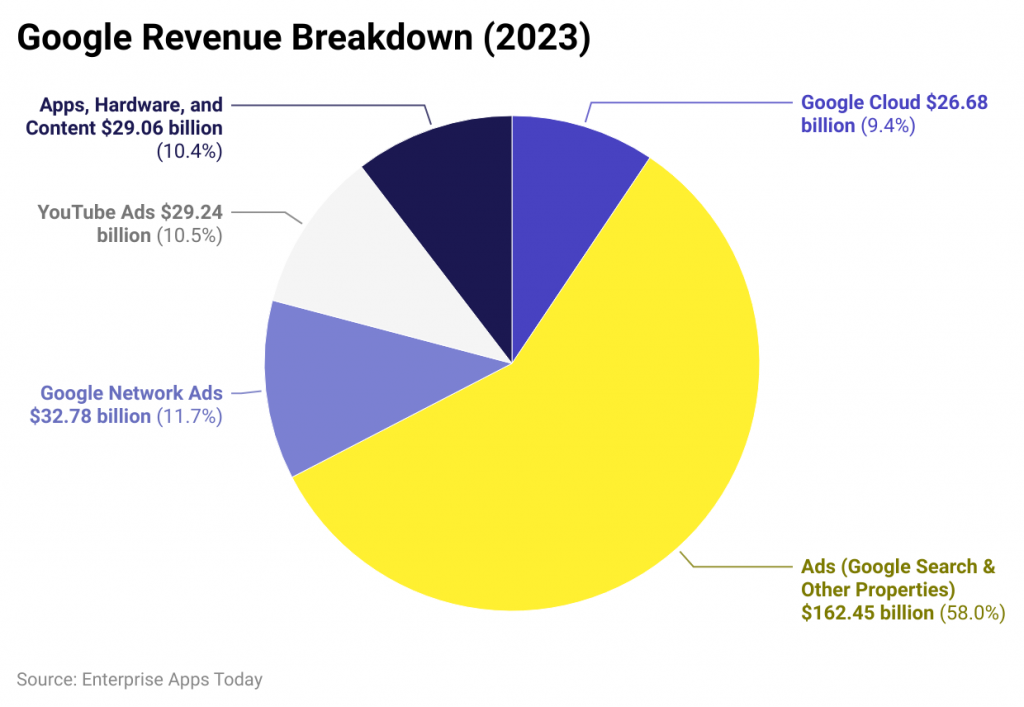

This point suggests that at best, the company turns a blind eye to generate higher revenues, including a package of malicious actors, or at worst, neglects security checks…
Youtube videos
Sources
| Title of Website | Link |
|---|---|
| Ars Technica | Mac info-stealer malware distributed through Google Ads |
| Latest Hacking News | New malware campaign spreads by exploiting Google Ads |
| Schneier on Security | Malware delivered through Google Search |
| Bleeping Computer (Ransomware) | Ransomware access brokers use Google Ads to breach your network |
| Bleeping Computer (Hackers push malware) | Hackers push malware via Google Search Ads for VLC, 7-Zip, CCleaner |
| Statista | Alphabet annual global revenue by segment |
References
| Title of Website | Link |
|---|---|
| Bleeping Computer (Fake Google Authenticator site) | Google Ads push fake Google Authenticator site installing malware |
| Bleeping Computer (Google Ads Tag) | Bleeping Computer Google Ads tag page |
| Malwarebytes Labs | Dozens of Google products targeted by scammers via malicious search ads |
